Simulation is a methodological approach for the analysis, design, and optimization of complex systems in domains such as industrial process design and urban mobility planning.
PDF: https://www.snap4city.org/download/video/digital-twin-simulation-2025-v01.pdf
The Snap4City BEFDIT (Behavior Execution Framework for Digital Twins) framework addresses key limitations of most of complex digital twin behavioral supports through the following contributions by providing:
- modular architecture to support multiple simulation tools through a range of interfaces (e.g., API, WS, files), enabling co-simulation and co-execution of different tools which can contribute to the same digital twin behavior. It is a way to ensure seamless integration of heterogeneous behavioral components embedded in simulation scenarios, enabling dynamic interactions, agent-level intelligence, and feedback mechanisms across different simulation scales.
- support for the integration on the front-end of the simulations / executors in “real time” and off-line via Web Interface. This point and previous are enabling solutions for co-working among experts on different fields/simulations models.
- support for the scalable management of the behavioral executions according to different business models in the range of “as a service” approach based on cloud/containers. Thus, opening the space to add other executors/simulations in the framework, supporting both open source and proprietary solutions. This is driver for reducing costs.
BEFDIT support the concept of Behavioral Executors, BEX, are capable of moving vehicle agents, computing routing for each vehicle, computing pollutant diffusion, making traffic flow predictions, computing emissions and costs, computing thermal evolution in building, computing the energy produced by irradiation, etc. Groups of BEX can be activated on demand.
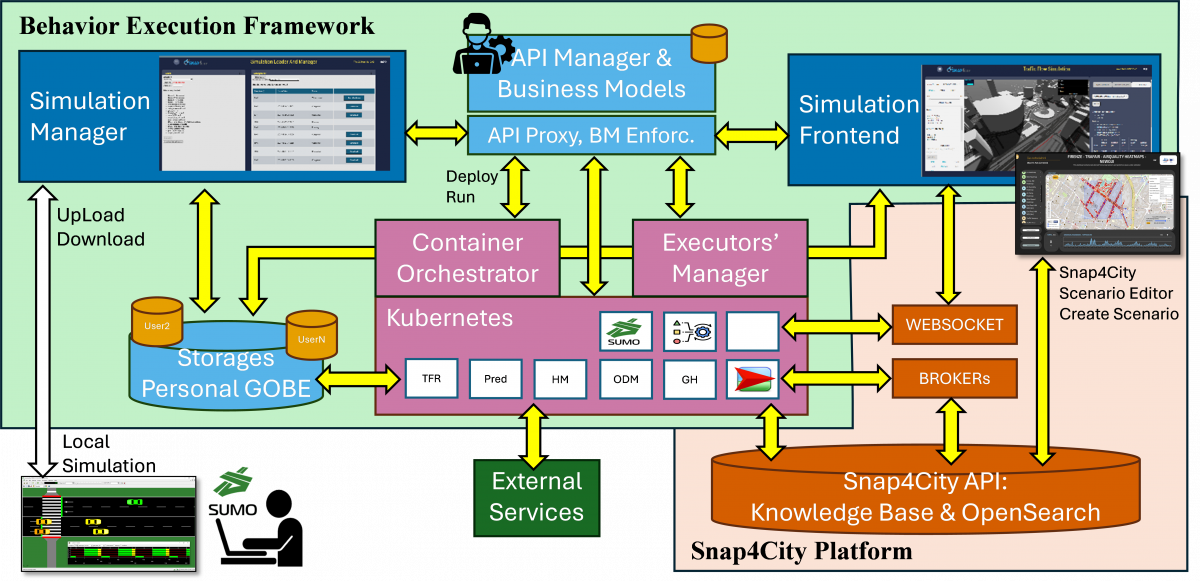
The solution enables users to configure and execute digital twins taking into account the behavioral aspects in the mobility and transport domain and it has been developed to extend the Snap4City open-source platform. BEFDIT consists of the following main components. Simulation Manager, which manages the data regarding simulation as they are the setup and results. It provides a user interface to allow the upload of files coming from local preparation of simulation and of download of results. Kubernetes, Container Orchestrator and Executors’ Manager (to manage BEXs). This area provides support on managing containers on which any kind of simulator and executor (BEX) can be deployed and run (in our cases: SUMO, traffic flow reconstruction, routing engines, predictions, etc. Each of them, may exploit services such as: those provide by Snap4City API, any other External Services via any protocol or API, IoT/WoT (internet/web of things) brokers, WebSocket (the latter two: to provide real time data/updates from/to the front- and back-end); and may access to the user’s personal storage. API Manager & Business Models provide support for defining which API can be exploited as well as by front end simulations and tools, according to a range of business models. Simulation Frontends is an exemplification of a large range of Snap4City Dashboards/Tools which can be built by exploiting API via Client-Side Business Logic in JavaScript, CSBL. Among the simpler front-end tools of Snap4City: the Scenario Editor of Snap4City which allows to extract/change a portion of the Digital Twin and save it on Snap4City storage, the MultiDataMap for rendering on maps/orthomaps: traffic, ODM, heatmaps, trajectories, sensor data, flows, vector fields, etc.; Synoptic frames in SVG; 3D rendering tools for cities; BIM viewers; Traffic Light Planer; Waste Management, Smart Light management; eShare for car sharing; etc.
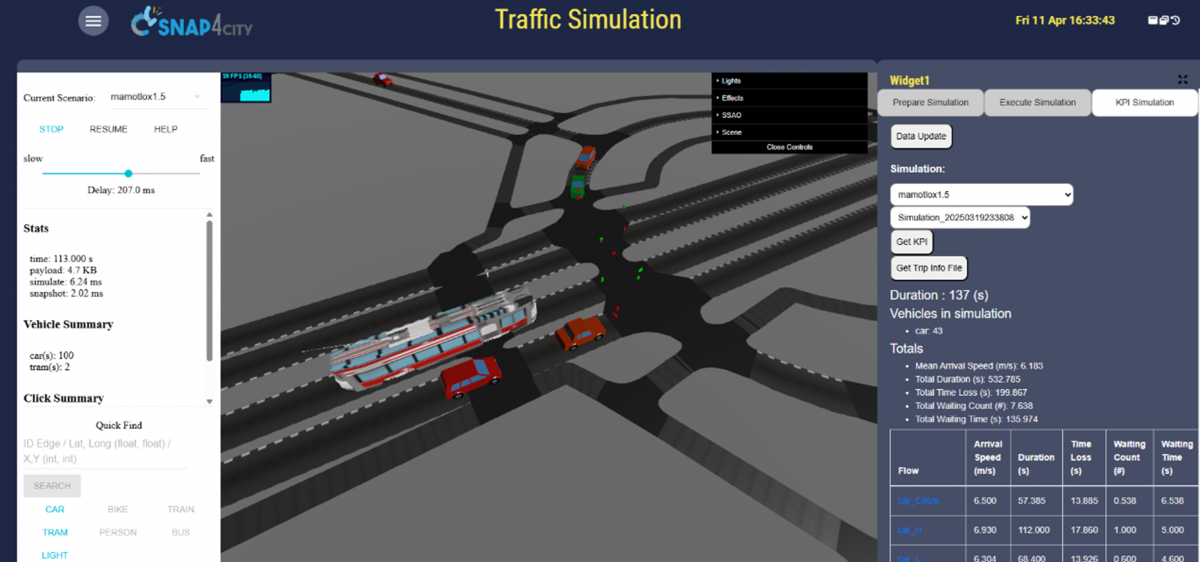
For example, BEFDIT allows the integration of simulated traffic data into the solution making it directly usable by existing tools for visualization, analytics, event management, or as input for new simulation and decision-support systems (see Figure). The use of simulated sensors enables several applications, including the validation of predictive models, testing of smart city services in controlled environments, provision of fallback data in case of real sensor failures, and support for digital twin configurations in urban mobility scenarios.
The BEFDIT is a scalable, modular, and interoperable environment designed to address the increasing complexity and fragmentation of simulation tools within smart city digital twin infrastructures, particularly for mobility and transport domains. BEFDIT successfully enables the integration and co-execution of heterogeneous behavioral models, supporting agent-based, discrete-event, continuous, and hybrid simulations, across multiple spatial and temporal scales. The framework's key contributions include: interoperability across diverse simulation tools through API-based communication and containerized deployments; Behavior execution as a service, leveraging business model integration for scalable and cost-effective simulation management; Real-time and offline co-simulation capabilities, supporting both human-driven what-if analyses and AI-driven optimization processes; Persistent, versioned simulation management, enabling reproducibility, scenario evolution, and extensive experiment tracking. BEFDIT's integration within the open-source Snap4City platform and its deployment in operational smart city contexts demonstrate its practical effectiveness. Use cases involving dynamic congestion management, real-time data generation, multi-simulator co-execution, and high-performance simulation orchestration highlight its adaptability, scalability, and robustness. Experiments and operational data collected over large-scale urban environments (e.g., Florence, Helsinki, Sweden, Greece) confirmed BEFDIT's capacity to handle millions of road elements and thousands of behavioral executions, with dynamic orchestration of cloud resources via Kubernetes clusters. These results validate the framework’s capability to enhance smart city decision-support systems by providing tactical and strategic planning tools based on automated, interoperable, and scalable digital twin simulations. Future developments will focus on expanding the ecosystem of integrated simulators and behavioral executors, strengthening AI-driven optimization loops, and further automating multi-domain what-if analysis processes. Additionally, efforts will be made to enhance multi-user collaboration features, privacy-preserving simulations, and broader exploitation across national and international smart city initiatives.
This result has been produced for the SASUAM scalability project, and for the OPTIFaaS Flagship project of CN MOST, the National Center on Sustainable Mobility in Italy (https://www.centronazionalemost.it/ ), and Snap4City as official infrastructure framework on which the experiments were conducted (https://www.snap4city.org). Snap4City is an open-source technology of DISIT lab.
PDF file: https://www.snap4city.org/download/video/digital-twin-simulation-2025-v01.pdf
This tool is accessible on Snap4City platform and some of its instances.
- This page: https://www.snap4city.org/1121
- https://www.snap4city.org/drupal/node/1014
- SASUAM: Solutions for Safe, Sustainable and Accessible Urban Mobility
- OPTIFaaS: Operation and Plan, Transport Infrastructure and Facilities Support as a Service
- CN MOST: https://www.centronazionalemost.it/