Snap4City has a number of tools and services which are divided in a number of Service Areas, that contribute to the system and to the production of IOT Applications and Dashboards by exposing API and Microservices.
All starts from the leg of the daisy, by using tools for creating IOT Applications, exploiting MicroServices and Dashboard.
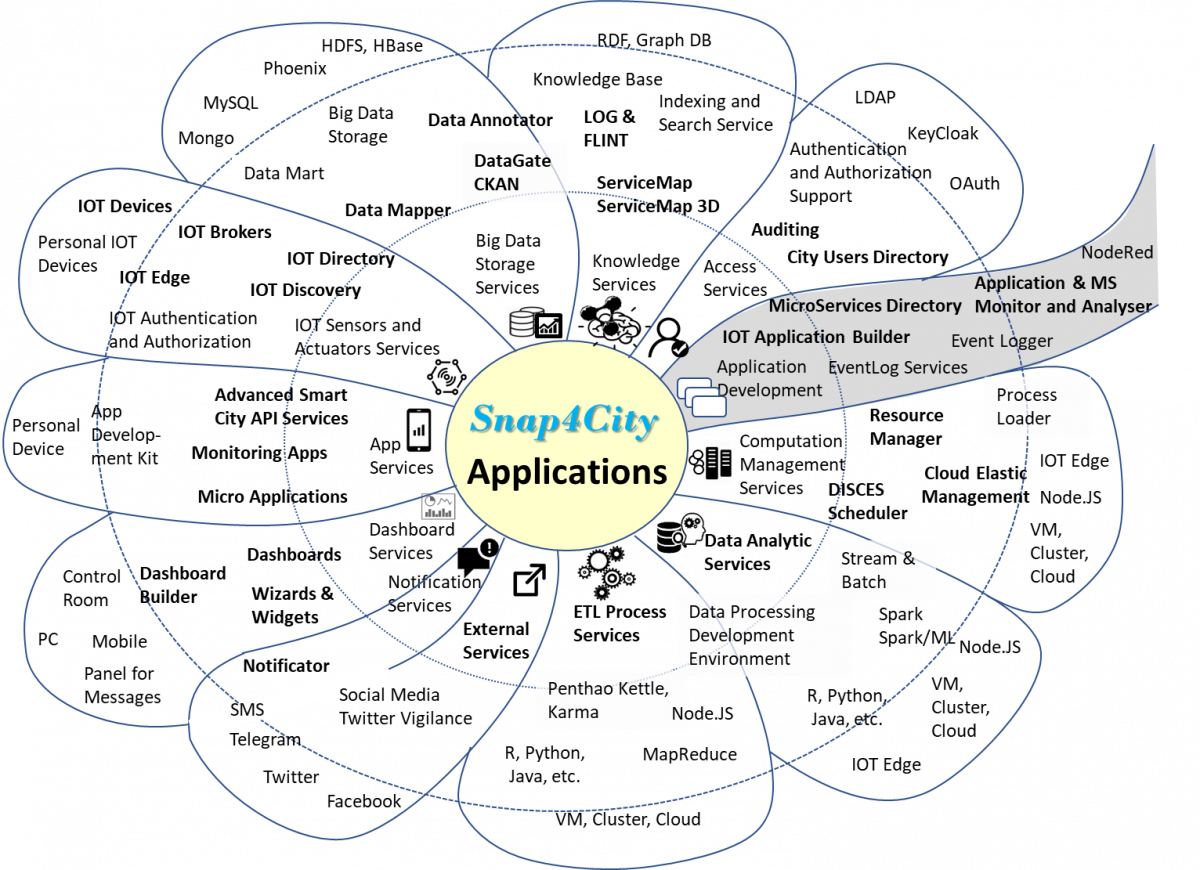
- Access Services: services and tools for enabling the authenticated access to data and services via some keys and certificates, according:
- Knowledge Services: semantic interoperability on concepts,
- enabling intelligence and reflection on Applications using geospatial reasoning;
- Semantic indexing and search: textual, structured, and geospatial;
- services and tools to manage a Knowledge Base, KB, all the information of the city including: sensors, IOT/IOE, actuators, MicroServices, street and structural elements, point of interest, areas, etc.; tools for browsing, querying and working with the city Knowledge Base such as: ServiceMap, ServiceMap 3D, LOG, FLINT;
- index and retrieve city elements by using several reasoners (Indexing and Search Services); every time a new element is added a new entity is indexed into the KB to enable semantic search and on SOLR for data browsing and drill down;
- Big Data Services (only save/load to some DB is available)
- services and tools for big data storage as: big data storage on distributed HA, DRS solution for structured and non-structured data;
- Load and save on Data Store: HDFS/Hbase via Phoenix, Banana, … save, access and retrieve data (for permanent and temporary data storage);
- collect data from external sources (DataGate/CKAN);
- drill down on data storage for IOT and ETL (Developer Dashboards)
- Drill down on semantic modelling and knowledge base: FLINT for query in SPARQL, LOD, RDF endpoint, ServiceMap, disit.org">LOG.DISIT.ORG;
- mapping data to other sources (DataMapper) for using other context data for validation and experiments;
- annotating data sets (DataGate) and data (DataAnnotator);
- Developer Dashboard: tools for drilling down into the data via SOLR index
- IOT Sensors and Actuators Services: a set of services and tools to
- access and listing of IOT/IOE elements into a directory (IOT Directory); They can be discovered and/or listed into a directory of sensors/actuators, using and exploiting multiple protocols to reach the devices.
- connecting and exploiting a set of IOT Brokers that may be connected a number of sensors and actuators;
- IOT Discovery, IOT Directory on a Knowledge Base with geospatial and description indexing;
- Wrappers from transcoding protocols with other protocols;
- Multiple IOT brokers for multiple protocols and formats;
- Support for end-to-end secure communication from IOT to Dashboards
- Traditional Web and Mobile App Services: a set of services and tools for preparing data for the Advanced Smart City API:
- exploiting Smart City Solution via Advanced Smart City API and MicroServices;
- communicating with users on their Web and Mobile Apps;
- monitoring their behaviour (according to the informed consent) enriching City User profile (City User Directory);
- developing web and mobile Apps (App Development Kit, ADK);
- engaging city users (Engagement Service); exploiting User Behaviour Understanding and collection of data
- Dashboard Services
- services for informing city users, Mobiles, Panels via: rendering data via multiple views/widgets: graphs, tables, maps, direct values, numbers, kiviat, trends, etc.;
- specific Widgets for collecting data from the users as sliders, text box, switches, etc.;
- Dashboards for all kinds of needs: controlling the city, for developer and for final users, personal dashboard.
- highly scalable on massive data rendering and H24/7 show on city operator, and Control Room
- Notification Services: (multichannel multimodal notification system, scalable)
- services and tools (Notificator) to send notification and alerts to City Users and operators about the events of critical conditions according to a City User Directory.
- notifications may reach the users by using multiple channels: email, phone, SMS, etc.
- Different notification models and tools for user kind and contexts
- External Services connecting any external service: social media, routing, etc. by Sync/Async
- services and tools for connecting external services. An example is the connection and exploitation of services of Twitter Vigilance as Social Media Service: a service to get Tweets and related metrics and data analytics tool, also capable to computer specific metrics, natural language processing, and sentiment analysis.
- Services can be reached with REST call, WS, etc.
- ETL Process Services: (for batch data ingestion and publication, transformation), Sync/Async, highly scalable
- services performing data transformations in batch on a parallel and distributed architecture, exploiting a mixt of solutions: Penthao Kettle, native language modules in R, Java, Python, etc.,
- Data gathering, data crawling, GTFS processing, DATEX, etc.
- Batch processing, massive processing
- Creating them via Visual programming, connection with Big Data (that is Penthao Kettle editor)
- executing them by means of the Computation Management Services, on the cloud infrastructure, in connection with Data Analytic Services;
- tools for their development in a sandbox the Data Processing Development Environment.
- services performing data transformations in batch on a parallel and distributed architecture, exploiting a mixt of solutions: Penthao Kettle, native language modules in R, Java, Python, etc.,
- Data Analytic Services: Sync/Async, highly scalable
- services implementing vertical algorithms such as: traffic flow reconstruction, parking free lot prediction, user behaviour analysis, routing (with several different parameters), traffic flow prediction, etc.;
- executing them by means of the Computation Management Services, on the cloud infrastructure, in connection with ETL Process Services;
- tools for their development in a sandbox the Data Processing Development Environment.
- Any analytics language and environment: R, Java, Python, Scala, R Studio, R Parallel, Machine Learning, Spark ML, Spark (available)
- Multiple Paradigm: R-Parallel, MapReduce, GPU, etc.
- Process Scheduling and Management via DISCES tool
- Computation Management Services: The typical smart city infrastructure may have several kinds of processes (period or sporadic, stream or batch), allocated on cloud (Virtual Machine) or on IOT Edge Computer, or even on external services (other public and private cloud, and/or third-party servers of some kind). They are services for controlling the execution of processes
- allocate and put in execution the different kinds of processes in any easy and transparent manner for the developers where they can be successfully executed (via DISCES),
- monitor their execution (Application Deployer and Resource Manager),
- allow process upload and monitoring results (Process Upload).
- process management, resource management, elastic computing
All the management aspects are not described in this view.