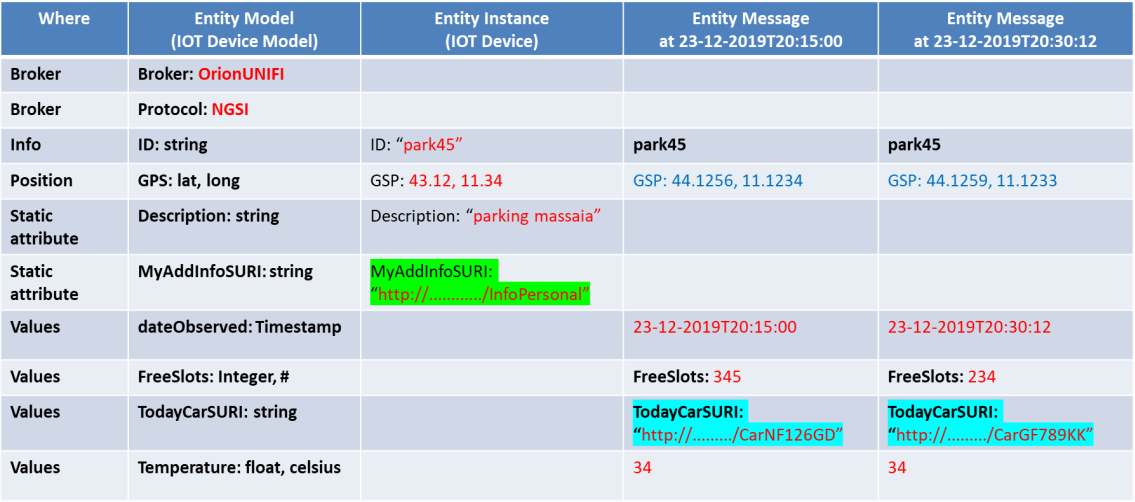
Thumb Rules on Snap4City from Data Modelling to Messages.
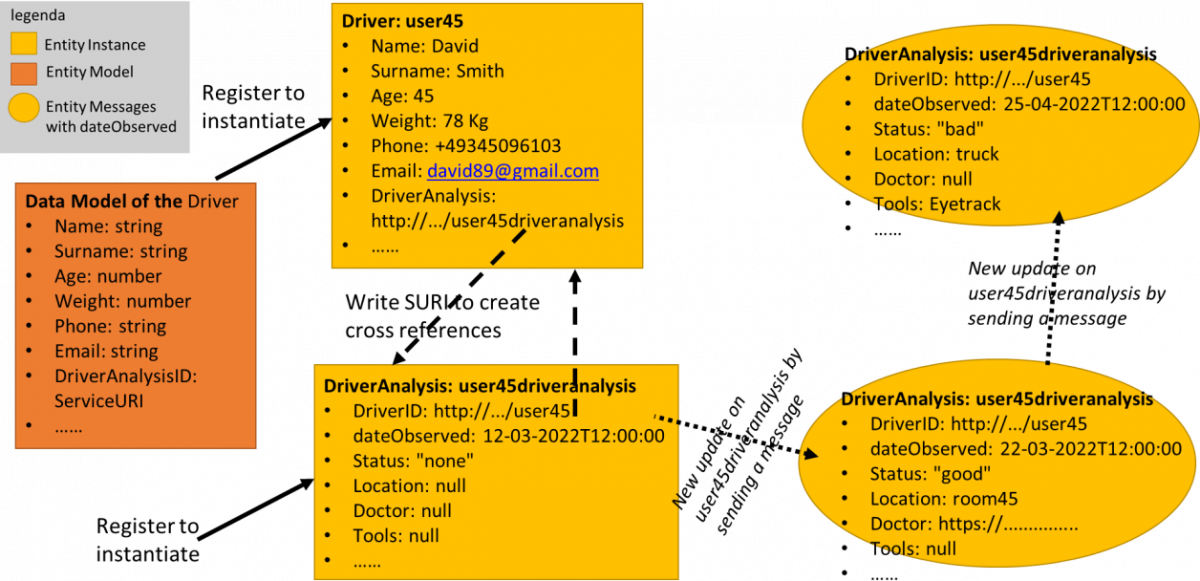
Figure: Example of relationships among Entity Model (IoT Device Model), Entity Instance (IoT Device),
Entity Messages (IoT Device Messages), according to the Snap4City terminology of 2023
In Snap4City:
- The relationships among models, entities/devices and messages are depicted in the previous Figure
- the Entity Models (IoT Device Models) can be simply instantiated from:
- FIWARE Smart Data Models, versioning, and harvesting the standard repository (from Entity Directory / IoT Directory tool of Snap4City)
- Entity Model / IoT Device Model which are accessible into the Snap4City environment (from Entity Directory / IoT Directory tool of Snap4City)
- Excel files by using Data Table tool, which extracts the model from the excel table and automatically creates IoT Device Model, IoT Devices and data attached to them
- Creating a custom Entity Model / IoT Device Model in standard Snap4City format (from Entity Directory / IoT Directory tool of Snap4City)
- the Entity Models can be customized.
- Each Entity Models / IoT Data Model is a template to produces Entity Instances / IoT Devices by registration (virtual or physical, does not matter). In the model creation one can specify static attributes describing
- nature/sub-nature
- a number of static variables, just defined once at the device creation.
- if the device can move or not (be mobile device or not), changing GPS data
- if the device is a certified one via BlockChain (beta version)
- Each Entity Models / IoT Data Model can
- Be modified in terms of attributes, variable, etc., without creating any change in the Entities Instances / IoT devices already produced in the past from the model.
- The Entity Instances / IoT Devices can be classified into
- Physical Entities (token, on board unit on the vehicle, device for assessing the drive attention, etc.). All Physical Entities are sending data on the platform on server via some Broker or other data ingestion process, for example via some local application, third party service, Edge solution, etc.
- Virtual Entities (Vehicle, Driver, DriverHealthiness, VehicleEvent, DriverEvent, DriverAnalysis). Virtual Entities are managed on server side for managing data and providing a set of user interface views for data entry (registering data) and for data rendering visualization.
- Entity Instances / IoT Devices can be created in Snap4City by means of:
- Manual production via Entity Directory / IoT Directory
- Massive production via:
- Data Table tool of snap4City
- Processing Logic / IoT App by using MicroService for
- Entity Instance / IoT Device production from Model
- Harvesting external Orion Brokers, also via Entity Directory / IoT Directory
- API and MicroServices
- Entity Instances / IoT Devices
- Can be modified in terms of variables and variable types without affective the Entity Model, neither the lost of pass data from Entity Messages.
- Cannot be modified in term of Entity/device name which is unique forever.
- Can be canceled, but actually the cancelation is not a physical delete of data and device, it is only a change of status on deleted, so that from administrator you can recover the case.
- Entity Messages are data messages sent over time changing the value of the Entity. They have to compliant with the Entity Instance, and may create Time Series as described in the next Figures.